Recently, a very sophisticated and targeted mobile attack on iOS using three zero-day vulnerabilities was discovered. The attacker can exploit 3 zero-day vulnerabilities (CVE-2016-4655, CVE-2016-4656, CVE-2016-4657) to silently jailbreak an iOS device and stealthily spy on victims, collecting information from apps including Gmail, Facebook, Skype, WhatsApp, Calendar, etc. Organizations who have their employees use their phones for both personal and professional communications are susceptible to such attacks.
NSO Group, an organization that claims to specialize in “cyber war,” created Pegasus, a mobile espionage product which uses three previously-unknown vulnerabilities in iOS. It takes advantage of : always connected (Wi-Fi, 3G/4G), voice communications, camera, email, messaging, GPS, passwords, and contact lists.
STAGE 1 Delivery and WebKit vulnerability: The attacker tricks a user to visit a malicious HTML page / file from his iPhone, that exploits a vulnerability (CVE-2016-4655) in WebKit (used in Safari and other browsers).
STAGE 2 Jailbreak: On successful exploitation of Safari browser, it downloads an obfuscated and encrypted package. Each time the package is downloaded, it is encrypted with unique keys, making traditional network-based controls ineffective. It contains the code that is needed to exploit the iOS Kernel (CVE-2016-4656 and CVE-2016-4657) and a loader that downloads and decrypts a package for stage 3.
STAGE 3 Espionage software: Post remote jailbrake, the espionage software, daemons, and other processes that are used are downloaded and hooks into the applications the attacker wishes to spy on. Additionally, stage 3 detects if the device was previously jailbroken through another method and, if so, removes any access to the device that the jailbreak provides, such as via SSH. The software also contains a failsafe to remove itself if certain conditions are present.
The target’s phone is remotely jailbroken and all personal information including Call lists, texts, calendar and contacts are all copied and sent to the attacker. It activates the phone’s cameras and microphone to snoop on conversations around the device. Victim’s movements are tracked and even messages from end-to-end encrypted chat clients are stolen. Competitors and nation-state actors are more interested in credentials and communications and business apps such as Gmail, Skype, WhatsApp, Calendar and others that may contain confidential technical, financial, or customer information.
In this mobile era, ideally an attacker would have access to more sensitive information than from a compromised laptop. Researchers from Lookout and Citizen Lab assisted Apple to fix the vulnerabilities and Apple has successfully patched all the 3 vulnerabilities in its 9.3.5 update. Hence, All iOS users should update to this version immediately.
More detailed technical analysis is available here.
 In an effort to improve targeted advertisements on the social network, Whatsapp now shares your mobile phone number with Facebook. WhatsApp will now pass on users' information onto its parent company, Facebook.
In an effort to improve targeted advertisements on the social network, Whatsapp now shares your mobile phone number with Facebook. WhatsApp will now pass on users' information onto its parent company, Facebook.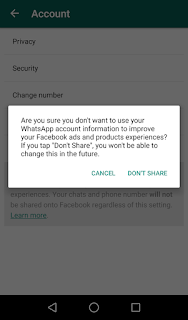
 If you are an existing user as of August 25, 2016, Whatspp allows you to decide whether Facebook should send you targetted ads and products experiences.
If you are an existing user as of August 25, 2016, Whatspp allows you to decide whether Facebook should send you targetted ads and products experiences.