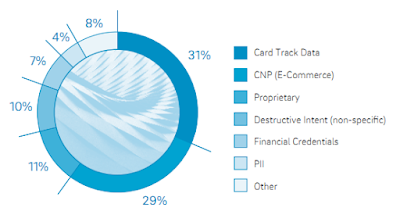
Although companies are always at risk for data security threats from the external hackers, employee activities cause a fair share of data breaches, too; simply cause people within the organizations do not understand the consequences of their erroneous actions or habit related to their company systems or critical data is alike if not excessive risk.
Every person within their organization has an access to some or the other company information which causes unauthorized release of data from within network. It is also seen that, although companies have protocols in place to prevent data breaches, many employees often break company policy. 53% of companies said employees use company-issued devices to send business-related information to personal email and cloud-based file-sharing accounts, such as Gmail and DropBox.
And for this reason, proper education for all the members of the organisation that encourages IT security safety is extremely important. Investing in security awareness sessions, professional development & trainings for existing staff can help to boost security. For anyone to stay ahead of hackers, people need to be up-to-date on this front.
Hackers will always be out there, adapting to the newest & most multifarious technology to set their targets. To counteract data breaches, we need to first work on the root cause of the problem i.e. invest in security and more emphasize the importance of education.
What do you think on this? Where to start with?
Take the below easy steps and there you are:
1) Awareness sessions about how a hacker can get in and poach your sensitive data
On an average, employees are aware of most likely keywords - virus, firewalls, malware, ransomware, cyberattacks, threats - but here again what does it all means has to explained to them at a basic level along with the consequences of the same. More highlighted area would be on how an external attacker can use them to get access to the company data.
2) Improvising employees erroneous actions
IT practices, protocols & polices could be well defined & handed over to the employees on the initial front itself. Very high chances, that won't come up with a surprise to you is of people violating these rules & policies set. For e.g.: Strict NO for attaching company files to any personal emails, uploading company files to cloud based sharing accounts, transferring data on non-encrypted USB's, etc.
For this yearly security awareness training & recapping sessions should be done as a part of company approach.
3) To lead people, walk besides them
By walking your talk, you become a person others want to follow. When leaders say one thing, but do another, they erode trust--a critical element of productive leadership.
As we all know, mostly management scares their employees into following policies but sometimes they tend to ignore it by themselves. The major turning issue here could be that if a manager violates a company policy while interacting with their employees, higher chances of employees do following the same path at their time of action. Showing employees that their concerns are a part of the IT security strategy is important because it diminishes the feeling that the policies are implemented to restrict them.
General things to be undertake would be likely:
• Elect who can access various systems and easily turn off someone’s access when it’s no longer needed.
• Regular password changes for highly sensitive accounts.
• Frequently rotate passwords to prevent brute-force or offline cracking attacks.
• Administer OTP's that will expire after a set period of time.
• Require users to present multiple types of authentication (two factor authentication) when logging into certain accounts.
Your mind is a storage room full of information, keep the door locked.
THINK before you CLICK, CONNECT & DOWNLOAD